
Many 3D print proponents claim that 3D printing is a good substitute for injection molding. Is that really the case? Now let's go and have a look. What's your opinion?
Material making (known as 3D printing) has had a big impact on the manufacturing sector. Those once needed hundreds of dollars, took several weeks of the hand, can now design in the morning and print at night, second days in the morning can reach the customer's hands.
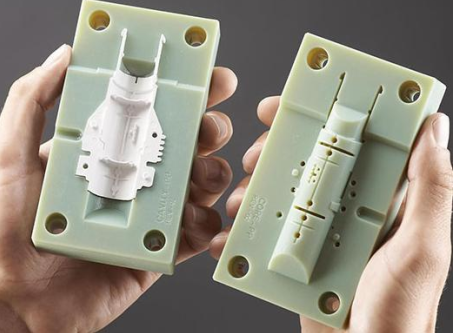
Some companies have been using 3D printing processes to make injection molds. It is no longer necessary to wait a few months for the manufacture of dies that can be used for production, or because the downstream design changes lead to significant changes in the amount of money invested in the mold or the uncertainties in the production layer. Whether mold verification or injection molding, small batch production, you can quickly 3D printing mold. If the mold has a problem or needs to modify the design, then print one and repeat the verification or production, that is. Am I right?
There is some truth to these arguments. Plastic 3D printed injection molds are somewhat like plastic sheds in our backyard. They are cheaper than metal sheds. Plastic sheds are constructed very fast and perform well under low loads. But if there's too much snow, they'll break into a house.
3D printing mold has its own place, and some enterprises in 3D printing mold application more successful. Supporters say the 3D printing die than traditional mold processing up to 90%, up to 70% cheaper. In some cases, this may be true, but it is important to understand the advantages / disadvantages of 3D printed plastic molds compared to metal molds.
True mold, really fast
ProtoLabs, a fast manufacturing company, has been manufacturing fast tooling injection parts since 1999. It provides molds for engineering plastics, metals, liquid silicone (LSR) and other materials. The moulds are mainly made of aluminum (in some cases, steel), and can be machined from several to 1000 parts, with a delivery time of 1-15 days.
Its industrial grade 3D printing services include stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Printable materials include thermoplastic materials like polypropylene and ABS, industrial grade nylon and metals (such as stainless steel, aluminum alloys and titanium alloys, etc.).
Since there is such a wide range of processing capacity, why not directly print mold, but machining mold?
Mold manufacturers should be vigilant
ProtoLabs engineers have been thinking about Printing dies, but after 16 years of rapid tooling business, some reasons still compel them to adhere to reliable fast injection molding processes:
Surface quality: 3D printing, layer by layer processing to obtain parts, which will lead to the surface of the products have step pattern effect. There is a similar problem with the direct print mold, which requires machining or sand blasting in the later stages to eliminate the tiny, serrated edges. In addition, holes smaller than 1mm must be drilled. Larger holes need reaming or drilling. The thread features need to be tapped or milled. These two treatments largely weaken the speed advantage of 3D printing dies.
Size factor: if you want to design a skateboard or plastic kit, the 3D print mold may be all right. The part size is limited to 10 cubic inches (164 cubic centimeters), roughly the size of grapefruit. And despite the high accuracy of current materials, it is still impossible to compare with machining centers and EDM equipment. The precision of the machined cavities is usually to 0.003 inches, and the parts are 59 cubic inches in volume, roughly 6 times the size of 3D printed parts.
High temperature environment: in order to ensure the material flow performance is good, the injection mold needs to be heated to very high temperature. Aluminum dies and dies usually experience 500F (260 degrees) or even higher temperature environments, especially in the manufacture of high temperature plastics such as PEEK and PEI (Ultem) materials. It is easy to produce thousands of parts with these metal molds and can be used as transition dies before the final mass production dies. Mold materials made from SLA or similar 3D printing processes are generally photosensitive or thermosetting resins, which are cured by UV light or laser. These plastic molds, although relatively rigid, are very quickly damaged in the thermal cycle of injection molding. In fact, under mild conditions, 3D printing dies usually fail within 100 times. High temperature plastics such as polyethylene or styrene. Glass filled polycarbonate and high temperature resistant plastics can even produce only a few parts.
Comparative cost: the primary reason for using 3D to print dies is because of their low cost. The production grade machine processing die cost is generally 20000 dollars or more, means that the same as 1000 U. S. dollars printing mold is similar. But this analogy is not fair. The evaluation of the printed mold Chen usually takes into account material consumption only and does not consider manual, assembly and installation, injection systems, and hardware. For example, ProtoLabsd's aluminum mold costs $1500 and can be used for production. What if more parts are needed? With 3D printing mold, you need to re print, assemble machine and test new mold every time you produce 50-100 products. On the other hand, without regard to the plastic used, the aluminum mold is usually in production and the 10000 parts are still in good service.
Product design: the principle and practice of traditional injection mold manufacturing has been more than a century of history, and the industry has made a thorough study of it. 3D printing mold is very new. For example, draft angle must be greater than or equal to 5 degrees, to meet the requirements of most aluminum mold. Plastic mold injection plastic parts are facing challenges, the number of plastic die thimble and installation location needs extra care.
The plastic mold (especially the high injection temperature) is more flexible to some extent in increasing the wall thickness and reducing the pressure. Gate design is also different, should avoid the use of tunnel and point gate. Direct gate, fan gate, and wing gate shall be increased to 3 times the normal size.
The flow direction of the polymer in the print mold shall be consistent with the 3D print line to avoid high fill due to viscosity and low pressure. The cooling system can improve the life of the die to a certain extent, but it will not obviously reduce the cycle times of the printing mold, because the heat dissipation ability of the plastic mould is not as good as that of the aluminum mold or the steel mould.
Opportunity
Although the rapid aluminum die has many advantages, in some cases, 3D printing mold will still play an important role. For manufacturers who have 3D printers and have enough time to explore how a printing mold works on an injection molding machine, perhaps they think they should print the mold directly.
Of course, mold designers have to understand how to make functional molds, and the redesign and manufacture of tooling costs a lot of cost. Related technical personnel and equipment are also necessary - mold sandblasting machine workers, thimble installation, injection molding machine operators, etc., because these parameters are set with the traditional mold is very different.
But wait - why don't you use DMLS? Why not print the metal mold directly? DMLS uses lasers and precision optical devices to coat and paint parts on small metal powder beds, producing fully dense commercial products that are widely used in aviation and medical fields. Some people predict that the mold of aluminum and die steel material may be printed directly in the future, providing ultra efficient conformal cooling channels, which will greatly reduce injection molding time and prolong the service life of dies. To some extent, DMLS direct printing die slow and expensive, usually only for mold is very small and complex, or those by traditional processing method of processing machine is difficult to manufacture the mold inserts.
Reliable measurement
In general, ProtoLabs thinks it's best to use DMLS, SLA, or other 3D printing techniques to do what they're good at: printing parts rather than moulds. However, if the following conditions are met, the 3D print injection mold will be a reliable alternative.
1)small batch and relatively simple parts, products require relatively large draft angle.
2) the tool and mould design team is familiar with the design principles of 3D printing dies.
3)personnel and equipment for processing and assembling plastic moulds.
Final design considerations. If you need to mold the long-term use, once 3D printing mold verified the design is reasonable, the next step is to adopt a more permanent mold material, such as aluminium or stainless steel, mainly because of small batch production of plastic mold production. Because 3D printing mold and traditional mold design is different, the project time and budget to consider a certain number of mold re design and test.


 PHONE:+86-20-82798231 82798232
PHONE:+86-20-82798231 82798232 FAX:020-82798208
FAX:020-82798208 E-MAIL:yf-hjy@yuanfang-group.com
E-MAIL:yf-hjy@yuanfang-group.com Address: Xintang town gurabardha Guangdong city of Zengcheng Province
Address: Xintang town gurabardha Guangdong city of Zengcheng Province